The Pauli Exclusion Principle is one of the most fundamental laws of nature. It plays a crucial role to the understanding of our universe & its impact can be seen in everything from the behavior of electrons in atoms to the structure of the stars in the sky. In this blog post, we will explore the Pauli Exclusion Principle in detail including its history, how it works & its impact on online readers. We will also discuss its benefits & limitations and answer some common questions about this important principle.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
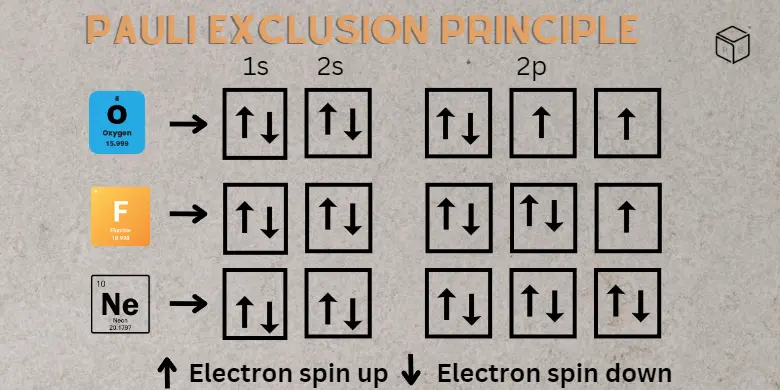
The Pauli Exclusion Principle is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that states no two fermions can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. In simpler terms, it means that two particles of the same type (such as electrons) cannot be in the exact same place at the exact same time with the exact same energy.
This principle was first proposed by the Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli in 1925 to explain the structure of atoms. At the time, scientists were trying to understand why atoms were stable & why electrons did not all collapse into the nucleus. Pauli proposed that electrons had a unique quantum property called spin, and that this spin prevented two electrons from occupying the same energy level within an atom.
How does the Pauli Exclusion Principle impact online readers?
The Pauli Exclusion Principle has significant impacts on the behavior of particles & by extension, on the world around us. It is responsible for many of the properties of matter including the chemical properties of elements & the structure of the periodic table. It also plays a crucial role in electronics and computer technology, as the behavior of electrons is central to the functioning of these devices.
In addition to its impact on the physical world, the Pauli Exclusion Principle has also had a significant impact on our understanding of the universe. By understanding the behavior of particles & the laws that govern their interactions, scientists have been able to make incredible advances in fields such as astronomy, quantum computing & materials science.
Examples of the Pauli Exclusion Principle in action:
The Pauli Exclusion Principle can be realized in many different areas of science & technology. Here are just a few examples:
The structure of atoms: The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells or energy levels, with not more than two electrons at each level. This is due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which prevents electrons from occupying the same energy level.
The properties of metals: Metals are good conductors of electricity because their electrons are able to move freely through the material. This is due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which allows electrons to occupy different energy levels & move through the metal.
Superconductivity: In certain materials, electrons are able to move through the material with zero resistance. This is due to a phenomenon known as Cooper pairing, which is a result of the Pauli Exclusion Principle.
Benefits and limitations of the Pauli Exclusion Principle:
The Pauli Exclusion Principle has numerous benefits, including its ability to explain the behavior of particles & the properties of matter. It has also led to many advances in technology, such as the development of transistors & other electronic devices.